Experiential learning is an educational approach that offers a refreshing departure from traditional classroom instruction by placing emphasis on hands-on experiences, active engagement, and practical application of knowledge. So “What is experiential learning?” This article will provide a comprehensive understanding of experiential learning, exploring its definition, principles, and the transformative impact it can have on learners. In addition, we will delve into the workings of experiential learning, uncovering the stages and processes involved in this dynamic educational approach. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what experiential learning entails and how it can revolutionize the way we learn and acquire knowledge. So, let’s VTJ explore this enlightening journey to discover the power of experiential learning and its potential to shape our educational experiences.
>>>Read more: Guide on How to Teach Vocabulary Effectively for Teachers
What Is Experiential Learning?
What Is Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning is an educational approach that focuses on learning through direct experience and active engagement. It goes beyond traditional classroom instruction by providing learners with opportunities to engage in real-world activities, reflect on their experiences, and draw meaningful conclusions. This approach emphasizes the importance of hands-on experiences, critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge in practical contexts. Experiential learning recognizes that learners acquire knowledge, skills, and attitudes more effectively when they are actively involved in their own learning process. It encourages learners to explore, experiment, and make connections between theory and practice, fostering a deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. By immersing themselves in real-world situations, learners develop practical skills, enhance their decision-making abilities, and gain a broader perspective on the subject matter. Experiential learning can take various forms, such as field trips, simulations, hands-on projects, internships, and collaborative activities.
>>>Read more: 120+ High and Middle School Debate Topics for Students
>>>Read more: What is blended learning? Types, Examples & Benefits?
How Does Experiential Learning Work?
Kolb’s (1984) model of learning illustrates the experiential learning process, as shown in the accompanying figure. This process involves the integration of various elements:
- Knowledge: this refers to the concepts, facts, and information that individuals acquire through formal education and previous experiences. It serves as the foundation for further learning and understanding.
- Activity: this involves applying the acquired knowledge in real-world situations or practical settings. By actively engaging in activities related to the subject matter, learners gain hands-on experience and develop practical skills.
- Reflection: after engaging in activities, learners engage in the critical analysis and synthesis of their knowledge and experiences. Reflection allows individuals to make connections, identify patterns, and extract meaningful insights. Through this process, new knowledge is created and understanding is deepened.
>>>Read more: How To Write a Curriculum in 8 Steps: A Complete Guide
>>>Read more: 14 Types of teaching methods for an effective lesson
The Experiential Learning Cycle
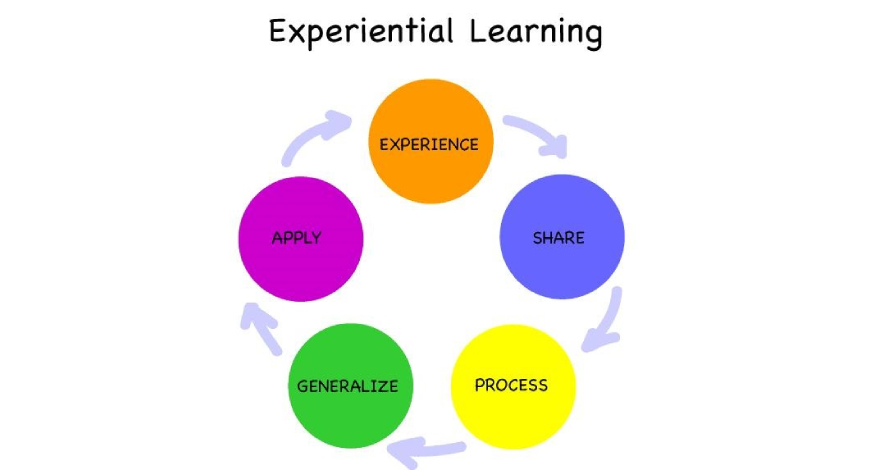
What Is The Experiential Learning Cycle?
Experiential learning operates on a cyclical process known as the Experiential Learning Cycle. This cycle consists of four key stages: experiencing, reflecting, conceptualizing, and applying. Let’s explore each stage in detail to understand how experiential learning works:
- Experiencing: the first stage involves actively engaging in real-world experiences or hands-on activities. Learners immerse themselves in practical situations, allowing them to directly interact with the subject matter. This could include field trips, simulations, experiments, or project-based tasks. By engaging in these experiences, learners gain firsthand knowledge and develop a deeper understanding of the topic.
- Reflecting: after the experience, learners engage in reflection. They take time to analyze and evaluate their observations, thoughts, and emotions related to the experience. Reflection encourages learners to critically examine their actions, identify patterns, and extract key insights. This stage promotes self-awareness, introspection, and the ability to make connections between the experience and existing knowledge.
- Conceptualizing: in the conceptualizing stage, learners analyze and conceptualize their reflections. They seek to understand the underlying principles, theories, and concepts that emerge from their experiences. This stage involves critical thinking, analysis, and the integration of new knowledge with existing knowledge frameworks. Learners develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter and identify broader implications and applications.
- Applying: the final stage of the Experiential Learning Cycle is applying. Learners take the knowledge, insights, and skills gained from their experiences and apply them in practical situations. This stage reinforces learning, as learners actively use their newfound knowledge to solve problems, make decisions, or engage in real-world scenarios. By applying what they have learned, learners solidify their understanding and develop practical skills.
>>>Read more: Why do you want to be a Teacher? 15+ Example Answers
>>>Read more: 40+ Preschool Teacher Interview Questions (+Answers)
The Experiential Learning Styles
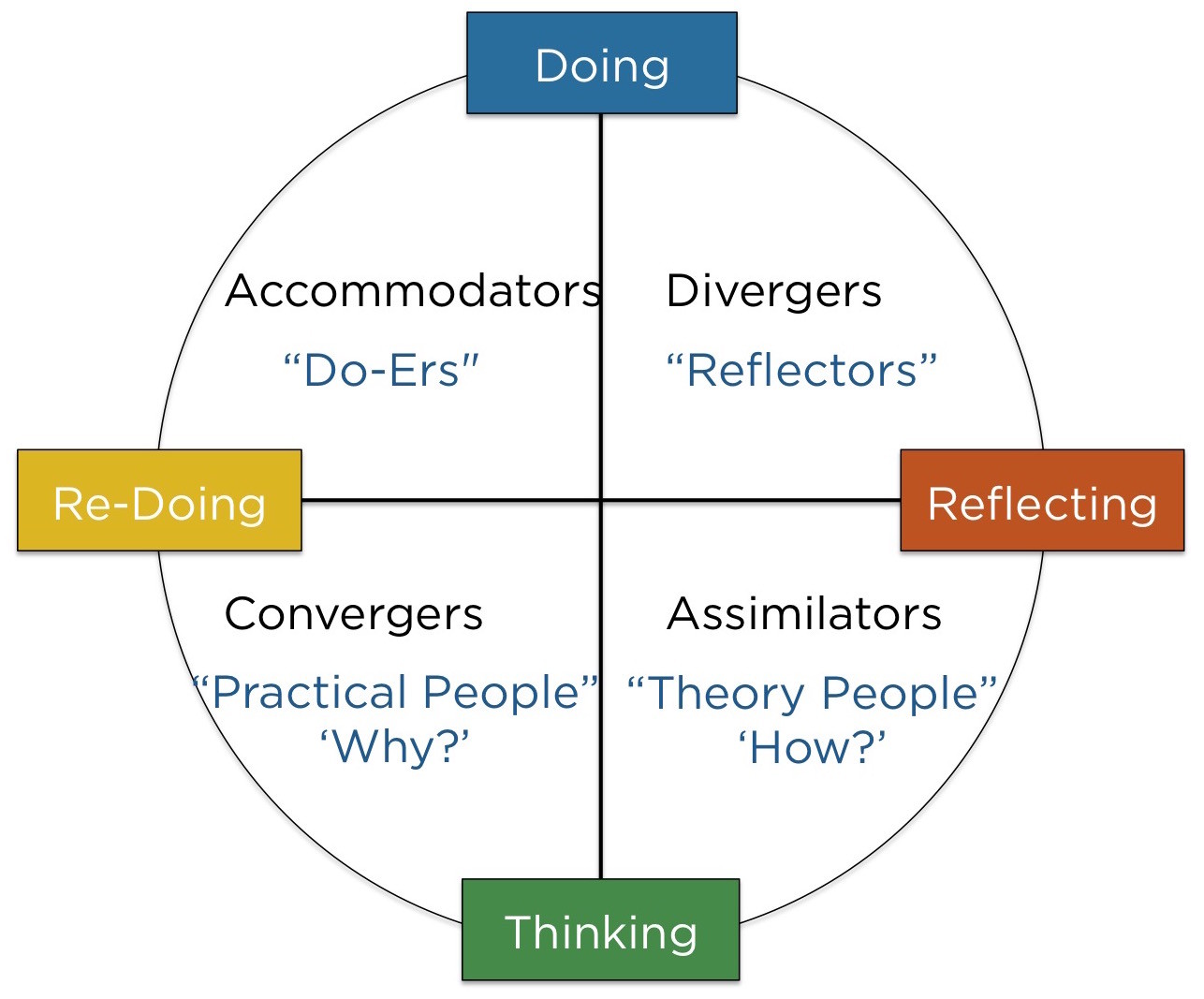
What Are The Experiential Learning Styles?
Experiential learning embraces diverse learning styles, recognizing that individuals have different preferences and strengths when it comes to acquiring knowledge. Here are some experiential learning styles:
- Diverging: Learners with a diverging style have a unique perspective and prefer to observe rather than take immediate action. They possess strong imaginative abilities and often work well in group settings. They focus on concrete learning and reflective observation, taking time to observe and understand the situation before engaging.
- Assimilating: This learning style involves learners who seek clear and concise information. They are more interested in abstract concepts and analytical models than in interpersonal interactions. Their learning process emphasizes abstract conceptualization and reflective observation, allowing them to grasp complex ideas and concepts.
- Converging: Converging learners excel at problem-solving and applying their knowledge to practical situations. They prefer technical tasks and enjoy experimenting with new ideas. Their learning style emphasizes abstract conceptualization and active experimentation, enabling them to find innovative solutions to real-world challenges.
- Accommodating: Learners with an accommodating style value practicality and enjoy taking on new challenges. They rely on intuition to solve problems and are comfortable with hands-on experiences. Their learning process involves concrete learning and active experimentation, allowing them to learn through direct engagement and trial and error.
>>>Read more: 4 Types of Learning Styles: How to Use VARK Model in Teaching
>>>Read more: 15+ Ways to build confidence in your ESL students
Experiential Learning Examples
Experiential learning brings education to life through immersive experiences that connect theory with real-world application. Here are some inspiring examples of experiential learning activities that foster active engagement and deeper understanding:
- Arts and Crafts Workshops: Integrate arts and crafts workshops that allow students to express their creativity and understand artistic concepts through hands-on activities.
- Language Immersion Activities: Create language immersion activities, such as language games, role-plays, or cultural exchanges, to enhance language learning through real-life interactions.
- Mock Trials or Courtroom Simulations: Organize mock trials or courtroom simulations to deepen students’ understanding of legal concepts and the justice system.
>>>Read more: How To Write a Lesson Plan in 6 Steps: The Complete Guide
>>>Read more: Practical Tips to Deal with Negative Teacher
Benefits Of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning offers numerous benefits to learners. One of the key advantages is enhanced engagement. By actively involving students in the learning process through hands-on experiences, experiential learning increases their motivation and enthusiasm for learning. This active engagement leads to a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Experiential learning also promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills as students are encouraged to analyze situations, make decisions, and apply their knowledge in real-world contexts. Additionally, experiential learning activities often involve collaboration and communication, allowing students to develop effective teamwork and interpersonal skills. By experiencing concepts firsthand and connecting theoretical knowledge with practical applications, students gain a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter and are better prepared for future challenges in their academic and professional lives.
>>>Read more: Teacher Burnout: Causes, Signs, and How to Avoid It
>>>Read more: What is TPR (Total Physical Response)? How can I use it?
>>>Read more: Different types of institutions to teach English in Vietnam
Experiential Learning Activities To Include In The Classroom

Experiential Learning Activities To Include In The Classroom
Incorporating experiential learning activities in the classroom can revolutionize the way students engage with the material and deepen their understanding of various subjects. Here are some enriching experiential learning activities to include in your classroom:
- Science Experiments: Conduct hands-on science experiments that allow students to observe and interact with scientific principles, fostering curiosity and a deeper appreciation for the subject.
- Role-Playing Simulations: Organize role-playing simulations that immerse students in historical events, literature, or real-world scenarios, encouraging them to take on different roles and perspectives.
- Field Trips: Plan educational field trips to museums, cultural centers, or relevant industries to provide students with real-world experiences and practical applications of their learning.
- Debates and Discussions: Conduct classroom debates and discussions on various topics to enhance critical thinking, communication skills, and the ability to consider multiple viewpoints.
- Entrepreneurship Projects: Have students create and manage their own small businesses or projects, cultivating entrepreneurship skills and problem-solving abilities.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences: Use virtual reality technology to take students on virtual field trips or simulations, providing immersive and interactive learning experiences.
- Outdoor Nature Studies: Conduct outdoor nature studies, exploring local ecosystems and biodiversity, promoting environmental awareness.
>>>Read more: 20+ Effective Classroom Management Strategies and Techniques
>>>Read more: What Is a Montessori School? Pros and Cons of Montessori School
The benefits of experiential learning extend beyond the classroom, equipping learners with critical skills, confidence, and a deeper understanding of the world around them. By embracing the experiential learning cycle and catering to diverse learning styles, educators can create a transformative learning environment that nurtures curiosity, critical thinking, and practical skills. VTJ helped educators unlock the full potential of experiential learning, where knowledge comes to life through immersive experiences.
FAQ
What are the 4 stages of experiential learning?
The experiential learning theory operates through four key stages: concrete learning, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. The initial two stages revolve around understanding and absorbing an experience, while the latter two stages center on the process of transforming and applying that experience.
What is an example of an experiential training method?
An example of an experiential training method is a team-building activity where employees participate in problem-solving challenges and collaborate to achieve common goals, fostering teamwork and communication skills.