
The ABC Model of Classroom Management: A Complete Guide for Teachers
The ABC model of classroom management is a systematic approach that helps teachers effectively manage student behavior. This practical framework analyzes three key components: Antecedents (what triggers behavior), Behavior (the actual student actions) and Consequences (what follows the behavior). By understanding this sequence, educators can create more positive learning environments and implement targeted behavioral interventions.
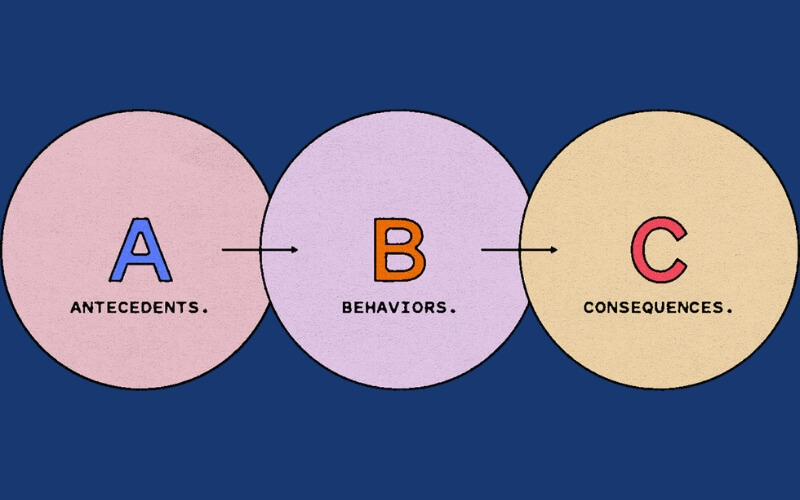
What is the ABC Model of Classroom Management?
The ABC model is a simple way to understand and manage behavior in the classroom. It breaks behavior into three parts: Antecedents, Behavior, and Consequences.
What are Antecedents in the ABC Model? Understanding Behavior Triggers
Antecedents are what happen right before a behavior. These are the triggers that lead to how a student acts. For example, it might be the teacher giving an assignment, asking a student to read out loud, or announcing it’s time to switch activities. By noticing these triggers, teachers can predict problems and make changes to avoid them.
How Does Student Behavior Function in the ABC Framework?
Behavior is the action or response of the student that happens because of the antecedent. It’s what the student does or says that needs attention. Examples include a student talking loudly while the teacher is speaking, getting out of their seat without permission, or making noises during a lesson. Recognizing the behavior helps teachers understand what needs to be addressed.
Why are Consequences Essential in Classroom Management?
Consequences are what happen right after the behavior. They show students the results of their actions. These can happen naturally or be introduced by the teacher or classmates. For example, the teacher might redirect the student, ask them to leave the classroom, or peers might respond to the disruption. Consequences help students learn what is acceptable and what isn’t.
The ABC model makes it easier for teachers to understand why certain behaviors happen and how to respond in a way that improves the classroom environment.
Explore More Teaching Tips: How to Keep Students Engaged in the Classroom?
How to Apply the ABC Model: A Step-by-Step Classroom Example
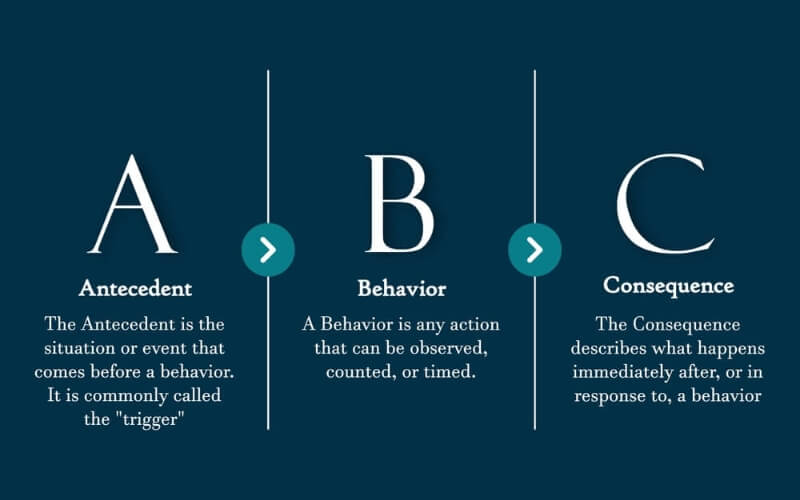
Here’s an example of how antecedents, behavior, and consequences work together:
- A (Antecedent): The teacher gives the class an independent assignment.
- B (Behavior): Johnny, a student, sits at his desk and starts drawing instead of working on the assignment.
- C (Consequence): The teacher ends up talking back and forth with Johnny about his behavior until the bell rings.
In this case, the teacher focuses on correcting Johnny’s behavior each time it happens. However, this can be tiring and repetitive. Without a clear plan to address the root of the issue, Johnny is likely to continue drawing instead of doing his work.
Explore More: Teacher Strengths and Weaknesses: How to Answer?
How to Effectively Document and Track ABC Model Components
To create an effective plan to address Johnny’s behavior, the teacher needs to understand exactly what is happening. This means gathering information about Johnny’s actions, when they occur, and how adults and classmates respond to his behavior. Essentially, the teacher needs to collect data on the ABCs: Antecedent, Behavior, and Consequence.
A simple way to collect this data is by using a data collection sheet created by the teacher. This sheet can track each instance of behavior by recording the antecedent, behavior, and consequence. Here’s an example of a blank data collection table:
| Student Name | Johnny |
| Overview of Situation | Johnny has become consistently disruptive, and nothing seems to work. |
| Date | A (Antecedent) | B (Behavior) | C (Consequence) |
| 12/12 | I give instructions for students to begin an assignment | Johnny sits at his desk and starts to draw | I engage in a conversation/argument about why he needs to be working |
| 15/12 | I give instructions for students to begin an assignment | He begins talking to his peers | I repeat instructions one-on-one to Johnny but he still does not start his work |
| 22/12 | I ask students to get out their math book | Johnny puts his head down on the desk | I ask him to sit up but he ignores me |
By using this method, the teacher can see a clear picture of the pattern of Johnny’s behavior. In this case, Johnny does not respond to the teacher’s instructions (the antecedent), and his behavior includes drawing, talking to peers, and ignoring instructions. The teacher’s responses (the consequences) include arguing, giving Johnny more individual instructions, and asking him to sit up. This data helps identify the problem areas and can guide the teacher in developing a better plan for addressing Johnny’s behavior.
Discover Related Guides: How to Assess Students Without Tests: 6 Effective Evaluation Methods
In conclusion, the ABC model of classroom management provides a practical framework for understanding and addressing student behavior. By focusing on antecedents, behaviors, and consequences, teachers can gain valuable insights into what triggers certain behaviors and how to respond effectively.







I was more inspiration from you